EXIF data is the hidden story behind every digital image. It’s a treasure trove of information, meticulously embedded within the file, detailing the camera settings, location, and even the time of capture. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of EXIF data, revealing its purpose, extraction, modification, and security implications.
Understanding EXIF data is crucial for photographers, journalists, and anyone working with digital images. It’s more than just technical specifications; it’s a window into the image’s history, a silent narrative woven into each pixel.
Introduction to EXIF Data
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data is a set of metadata embedded within digital image files. This data provides information about the image’s creation, including details about the camera, settings, and shooting conditions. This detailed information is crucial for understanding and managing digital images effectively.EXIF data plays a vital role in digital photography by offering comprehensive details about the image’s capture.
It enables users to understand the specific conditions under which a photo was taken, such as the camera model, shutter speed, aperture, and focal length. This knowledge can be invaluable for photo editing, archival purposes, and understanding the artistic intent behind a particular image.
EXIF Data Purpose and Function
EXIF data’s primary function is to store and provide access to critical information about the digital image itself. This information is often used to enhance image management, analysis, and understanding of the capture process. It’s crucial for both professional and amateur photographers alike.
Types of Information in EXIF Data
EXIF data encompasses a wide array of information. This data helps users understand the camera settings, technical details of the capture, and even geographic location.
- Camera Settings: EXIF data often includes the camera model, lens used, shutter speed, aperture, ISO, and focal length. This information is fundamental for evaluating the technical aspects of an image and replicating similar results.
- Date and Time of Capture: The precise date and time the image was taken are typically included. This is crucial for accurate image organization and chronological ordering.
- GPS Data: If the camera has GPS capabilities, EXIF data might include the geographic coordinates of the location where the photo was taken. This information is valuable for geolocation tagging and historical context.
- Image Dimensions and Resolution: EXIF data often includes the image’s width, height, and resolution, which are essential for printing, resizing, or adjusting the image in various applications.
Common EXIF Data Fields
The following table presents a concise overview of some common EXIF data fields:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Image Width | The width of the image in pixels. |
| Image Height | The height of the image in pixels. |
| Date and Time Original | The date and time the image was originally captured. |
| Shutter Speed | The duration the camera’s shutter remained open. |
| Aperture | The size of the opening in the lens. |
| ISO Speed | The sensitivity of the camera’s image sensor. |
| Focal Length | The distance from the lens to the image sensor. |
| Flash | Indicates whether a flash was used. |
| GPS Latitude | The latitude of the location where the photo was taken. |
| GPS Longitude | The longitude of the location where the photo was taken. |
Extracting EXIF Data
Extracting EXIF data is a crucial step in analyzing image metadata. This process allows users to access and interpret information embedded within image files, revealing details about the capture conditions, equipment, and other relevant parameters. Understanding how to extract this data is valuable for photographers, researchers, and anyone working with image files.Various methods and tools exist for extracting EXIF data.
Different methods cater to different needs and preferences, ranging from simple command-line utilities to comprehensive graphical interfaces. Choosing the right approach depends on the user’s familiarity with the tools and the complexity of the task at hand.
Methods for Extracting EXIF Data
Several approaches exist for extracting EXIF data. Command-line tools offer a flexible and powerful way to extract information programmatically. Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) provide a user-friendly interface for those who prefer a visual approach. Specialized software packages provide comprehensive solutions, integrating EXIF extraction with other image manipulation tasks.
Command-Line Tools
Command-line tools offer a highly customizable and efficient way to extract EXIF data. These tools are often favoured by programmers and users who need to automate tasks or integrate data extraction into larger workflows. For instance, `exiftool` is a powerful command-line tool that allows for detailed extraction and manipulation of EXIF data.
Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs)
Many image editors and viewers include built-in features for displaying EXIF data. These tools typically present the data in a user-friendly format, making it easily accessible and understandable. Examples include Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, and various image viewers available on different operating systems. Often, these GUIs present the EXIF data in a formatted table, enabling easy comprehension.
Specific Tool: ExifTool
ExifTool is a widely used command-line tool for examining and modifying EXIF data. It supports a vast range of image formats and metadata types. To extract EXIF data using ExifTool, follow these steps:
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Navigate to the directory containing the image file.
- Use the command `exiftool -s filename.jpg` (replacing `filename.jpg` with the actual filename). The `-s` option ensures the output is displayed in a human-readable format.
- The command will display the EXIF data for the specified image file.
Comparison of Extraction Tools
This table summarizes various EXIF extraction tools and their key capabilities.
| Tool | Type | Capabilities | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| ExifTool | Command-line | Supports numerous image formats, metadata modification, and detailed data extraction | Moderate (requires command-line familiarity) |
| Adobe Photoshop | GUI | Displays EXIF data within the application | High (user-friendly interface) |
| GIMP | GUI | Displays EXIF data within the application | High (user-friendly interface) |
| ImageMagick | Command-line | Powerful image manipulation tool, can extract EXIF data | Moderate (requires command-line familiarity) |
Understanding EXIF Tags
EXIF tags are crucial components of image metadata, providing valuable information about the image’s creation and capture. They essentially act as a detailed logbook, recording settings, conditions, and other relevant data. This allows for a deeper understanding of the image’s history and the process behind its creation. Knowing how to interpret these tags can greatly enhance image analysis and potentially even aid in image restoration.Understanding EXIF tags goes beyond simply knowing what they are; it’s about understanding their significance in the context of the image itself.
By looking at the various tags, one can gain insights into the photographer’s intentions, the technical conditions during capture, and even subtle clues about the environment where the picture was taken. This knowledge can be instrumental in various applications, from photo editing to historical research.
DateTimeOriginal
This tag records the precise time and date the image was created. Its significance lies in establishing the temporal context of the image. Knowing when a photograph was taken can help researchers and historians place the image within a specific historical period, aiding in the understanding of events and circumstances. This is particularly useful in historical records, news archives, and even personal photo collections.
For example, a photograph tagged with DateTimeOriginal of “2023-10-27 14:30:00” clearly indicates the date and time the image was captured.
ApertureValue
This tag specifies the aperture setting used during exposure. Aperture, measured in f-stops, controls the amount of light entering the camera. A smaller f-stop number (e.g., f/2.8) allows more light, resulting in a shallower depth of field, while a larger f-stop number (e.g., f/22) allows less light and produces a greater depth of field. This tag directly impacts the image’s depth of field, a crucial element for many photographic styles.
A high aperture value suggests a more focused subject against a blurred background.
FocalLength
This tag records the focal length of the lens used to capture the image. Focal length, measured in millimeters, determines the magnification and perspective of the image. A shorter focal length (e.g., 24mm) provides a wider field of view, while a longer focal length (e.g., 300mm) provides a more zoomed-in perspective. The focal length directly influences the image’s composition and the overall impression it conveys.
A 50mm focal length is often considered a “normal” perspective for a full-frame camera.
Relationship Between Tags
The interplay between these tags, and others, provides a comprehensive picture of the photographic process. For example, the ApertureValue and FocalLength tags work together to influence the depth of field. A wider aperture (smaller f-stop number) with a shorter focal length tends to result in a shallower depth of field. The DateTimeOriginal tag complements these by placing the image in a specific timeframe.
Understanding these relationships helps in assessing the quality and intent of the image.
Interpreting EXIF Data
Interpreting EXIF data involves understanding the numerical values and their corresponding units. For instance, the ApertureValue tag, often represented by a numerical value, correlates to a specific f-stop setting. This numerical value is associated with a physical aperture setting. By examining the specific values within these tags, one can gain insights into the photographer’s choices and the technical conditions of the image capture.
Modifying EXIF Data

Altering EXIF data within image files offers a range of possibilities, from simple adjustments to more complex manipulations. This process can be useful for various applications, such as managing copyright or adding metadata to track the image’s history. Understanding the methods and potential implications of modifying EXIF data is crucial for anyone working with digital images.Modifying EXIF data can be achieved using a variety of software tools and scripting languages.
The methods vary in their complexity and capabilities, affecting the level of control and precision in modifying the data. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific needs and the level of expertise in image manipulation.
Techniques for Modifying EXIF Data
Various techniques exist for altering EXIF data within image files. These techniques range from straightforward graphical user interfaces to more advanced scripting approaches. The choice of technique often depends on the desired level of control and the complexity of the modification.
Software Tools for EXIF Modification
Numerous image editing software packages provide tools for manipulating EXIF data. These tools typically offer a user-friendly interface for modifying various tags, making them suitable for users with less technical expertise. Some widely used image editors offer comprehensive EXIF editing options.
Scripting Languages for EXIF Modification
Scripting languages like Python, with libraries like `exiftool`, offer greater flexibility and control over EXIF modification. These approaches are generally preferred for more intricate modifications or automation tasks. This approach empowers users to craft custom scripts for diverse needs.
EXIF data’s crucial for understanding image details, but sometimes it’s a bit buried. Snapseed, a powerful mobile photo editor, lets you access and adjust these details with ease. This makes managing EXIF data more straightforward, especially for photographers looking for quick editing options.
Example Scenarios for Modifying EXIF Data
Modifying EXIF data can be applied to various scenarios. For instance, copyright management can be enhanced by adding or modifying copyright information within the EXIF data. Similarly, image history can be recorded by tagging details such as date of creation, location, or camera settings. These applications are useful for managing intellectual property and preserving image provenance.
Comparison of EXIF Modification Methods
| Method | Ease of Use | Level of Control | Automation Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Editing Software | High | Medium | Low |
| Scripting Languages (e.g., Python with exiftool) | Medium | High | High |
This table summarizes the key differences between modifying EXIF data using software tools and scripting languages. Software tools are easier to use but offer limited control, whereas scripting languages allow for greater precision and automation. The choice depends on the desired level of control and the complexity of the modification.
Security Implications of EXIF Data
EXIF data, while primarily designed for image metadata, presents potential security vulnerabilities if not handled carefully. This data can contain sensitive information, such as location data, camera model, and timestamps, which can be exploited by malicious actors. Understanding these risks is crucial for safeguarding digital assets and maintaining privacy.
Potential Security Risks
EXIF data can leak sensitive information about the image’s origin and capture conditions. This information, when combined with other data points, can reveal details about the photographer, the location of the image, and the time of capture. Malicious actors can use this information to target individuals, steal intellectual property, or commit other crimes.
Exploitation Techniques
Malicious actors can leverage EXIF data in various ways. For instance, an attacker could use location data embedded in EXIF to target individuals in a specific geographic area for phishing attacks. Similarly, timestamps could be used to determine the time of an event, allowing an attacker to predict future actions or activities. EXIF data can also be used to corroborate or create false evidence in legal proceedings.
For example, an attacker might manipulate EXIF data to suggest an image was taken at a particular time, even if it was taken later.
Tracking and Tracing Images
EXIF data’s inherent tracking capabilities are a significant concern. The inclusion of GPS coordinates, camera model, and timestamps provides a trail that can be followed to identify the origin and movement of images. This data can be used to track the movement of individuals or assets, potentially revealing sensitive information about their activities.
Security Measures, EXIF data
Various security measures can mitigate the risks associated with EXIF data manipulation. Robust image editing software often allows for the removal or modification of EXIF data. This is a basic but important method of protection. Furthermore, secure image hosting platforms may employ automated checks to detect and prevent the upload of manipulated images. Specialized tools are also available for examining and validating EXIF data, enabling users to identify potential anomalies and manipulations.
EXIF Data and Image Editing Software
Image editing software frequently interacts with EXIF data, either preserving, modifying, or discarding it. Understanding how these applications handle EXIF data is crucial for maintaining image metadata and avoiding unintentional alterations. This section explores the intricate relationship between image editing tools and EXIF information.
Image Editing Software’s Handling of EXIF Data
Image editing software, ranging from basic photo editors to professional graphic design suites, typically allows users to view and modify EXIF data. The display methods vary based on the specific application, but often include a dedicated panel or menu option to access EXIF details. This access facilitates the ability to inspect the camera settings, location, and other important information associated with the image.
Effects of Editing Tools on EXIF Data
Different image editing tools affect EXIF data in diverse ways. Basic adjustments, like cropping or resizing, often leave the core EXIF data intact. However, more substantial modifications, such as applying filters or significant color adjustments, can potentially alter the EXIF data. Some tools may automatically update EXIF tags reflecting the modifications. Others may retain the original EXIF data, creating a historical record of the image’s original metadata and subsequent edits.
This flexibility is important for archival purposes and understanding image history.
Embedding or Removing EXIF Data in Image Editing Software
Image editing software provides mechanisms for users to embed or remove EXIF data. The exact procedures differ across programs. Some applications offer a direct option to edit EXIF tags, allowing users to manually add, update, or delete metadata. Other tools may require more complex maneuvers, such as using specific menus or functions to handle EXIF manipulation. In general, image editing software aims to give users control over metadata, whether for maintenance or security reasons.
Comparison of Image Editing Programs and EXIF Data
| Image Editing Program | Handling of EXIF Data | Effects of Editing | Embedding/Removal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Photoshop | Comprehensive view and modification of EXIF tags. Allows manual insertion and deletion of tags. | Significant edits (e.g., filters, adjustments) might update some tags; others remain unchanged. | Direct access to EXIF panel for modification. |
| GIMP | Provides a way to view and edit EXIF data. Offers basic tag manipulation. | Changes to image size, cropping, and simple adjustments usually don’t affect EXIF data significantly. | User-accessible options for editing or removing EXIF information. |
| Paint.NET | Limited EXIF data display and modification options. | Minor edits are unlikely to impact EXIF data; major changes might result in altered or removed tags. | Potentially limited ability to manipulate EXIF, depending on the specifics of the program version. |
Note: The table above provides a general overview. Specific features and functionalities may vary between different versions of these programs and other image editors.
EXIF Data and Image Sharing Platforms
Image sharing platforms have become ubiquitous, facilitating the rapid dissemination of visual content. Crucially, these platforms often interact with and manage EXIF data embedded within images, affecting how images are displayed and utilized. This section explores how various platforms handle and utilize this metadata.
EXIF Data Handling by Platforms
Image sharing platforms typically handle EXIF data in a variety of ways. Some platforms automatically display relevant EXIF information, such as camera model, shutter speed, and aperture, directly within the image viewing interface. Other platforms might store this data but not present it to the user unless specifically requested. The manner in which EXIF data is handled often depends on the platform’s design goals and user experience considerations.
Display of EXIF Data in User Interfaces
Platforms employ various approaches to display EXIF data to users. Some platforms offer a dedicated EXIF viewer, enabling users to inspect the metadata associated with an image in a detailed manner. Other platforms might display a condensed view, presenting only key EXIF information, like the date and time of capture. The level of detail displayed often depends on the image’s context and the platform’s user interface design.
For example, a social media platform might show a simplified view, while a professional photo-sharing site might provide more comprehensive EXIF details.
Platform-Specific EXIF Data Policies
Different image sharing platforms adopt varying policies regarding EXIF data. Some platforms might allow users to modify or delete EXIF data; others might prohibit such actions to maintain data integrity or adhere to user agreements. This approach to EXIF management can influence how users interact with and share images on the platform. For instance, a platform focused on raw image sharing might retain all EXIF data for image quality control, whereas a platform focused on user-generated content might remove or simplify EXIF information to enhance user experience.
Summary of Platform EXIF Data Handling
| Platform | EXIF Data Display | EXIF Data Modification | Specific Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limited display of basic EXIF data (date, time) | No direct modification; some tools might allow manipulation of metadata, but not directly within the platform | Focus on user experience and visual presentation; metadata often simplified for mobile-first approach | |
| Flickr | Comprehensive EXIF data display, including advanced settings | Users can typically view, but not modify EXIF data in the standard interface; advanced users may have access to tools for modification | Primarily a platform for photography enthusiasts and professionals; maintaining the original data is essential for accurate image provenance |
| Dropbox | Limited display; primarily metadata associated with file creation and last modification | No direct modification of EXIF data; users can modify file attributes (not metadata) | Focus on file storage and sharing; image quality control is not a primary function. EXIF data might be used for backup and versioning |
Advanced EXIF Data Topics
EXIF data, while fundamental to image metadata, extends beyond basic camera settings. Advanced formats and structures, coupled with the use of GPS data and camera-specific settings, provide rich insights into the image’s creation and context. Understanding these intricacies is crucial for advanced image manipulation and analysis.
EXIF Data Formats and Structures
Different camera models and software applications might use slightly varying EXIF structures. While the core structure remains consistent, the inclusion of additional tags can differ. This variance in structure necessitates careful consideration during data interpretation, especially when using diverse image collections. Variations in structure can impact how software tools interpret and manipulate the data. This often necessitates careful validation and error handling within software applications that work with EXIF data.
GPS Coordinates in EXIF Data
GPS coordinates embedded in EXIF data offer significant practical applications. Precise location data can pinpoint the geographical coordinates where an image was captured. This is invaluable for geotagging images, creating thematic maps, or historical record-keeping. For instance, a photographer documenting a natural disaster could use the GPS data to precisely correlate the location of damage with the image.
Similarly, researchers studying wildlife behavior can use GPS data to track animal movements based on photographs.
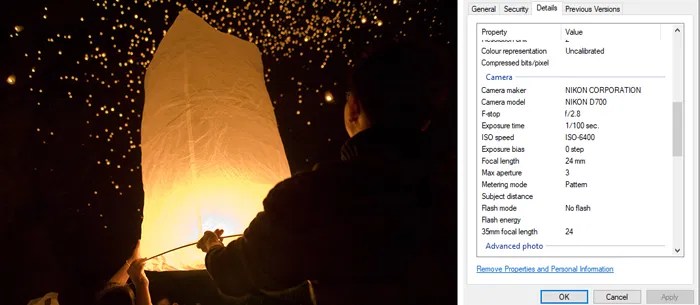
Camera Settings and EXIF Data
Camera settings directly influence the EXIF data recorded. Shutter speed, aperture, ISO, and white balance settings are all captured as part of the metadata. Understanding these settings is vital for evaluating the image’s technical characteristics and the environmental conditions during capture. A photograph taken with a slow shutter speed and high ISO might indicate a low-light environment, impacting how the image was captured.
Analyzing these settings in conjunction with the image can help determine the appropriate exposure and lighting conditions.
Software’s Role in Interpreting and Manipulating EXIF Data
Specialized software plays a critical role in interpreting and manipulating EXIF data. Image editing applications, as well as dedicated EXIF viewers, provide tools for inspecting, modifying, and extracting data. Such software enables users to understand the technical specifications of a photo and make adjustments as needed. Sophisticated image management tools often allow users to search, filter, and organize images based on EXIF data.
Practical Applications of EXIF Data
EXIF data, embedded within digital images, provides a wealth of information beyond the visual content. This metadata can significantly aid various fields, from journalistic investigations to forensic analysis, by offering crucial contextual details. Understanding and utilizing this data effectively unlocks a powerful tool for problem-solving and verification.The practical applications of EXIF data span across diverse industries, offering valuable insights into image creation and capture.
This metadata acts as a timestamped record of the image’s journey, providing context, location, and technical details. By carefully examining this data, professionals can glean a deeper understanding of the image’s origin and history, leading to more accurate interpretations and conclusions.
EXIF Data in Journalism
EXIF data can be instrumental in verifying the authenticity and provenance of images used in news reporting. By examining metadata, journalists can determine if an image is genuine, whether it has been manipulated, and establish the conditions under which it was captured. This verification process helps maintain journalistic integrity and credibility. For instance, a news organization could verify the time and location of a photograph to ensure it accurately depicts the reported event.
This is crucial in avoiding misinformation and ensuring the reliability of published content.
EXIF Data in Photography
EXIF data serves as a comprehensive record for photographers. It provides valuable insights into the technical aspects of image capture, allowing photographers to analyze their work and refine their techniques. For example, examining shutter speed and aperture settings allows photographers to understand the exposure conditions and adjust their settings for future shots. Analyzing EXIF data across a series of photographs can reveal trends in a photographer’s style and preferred settings.
This can be invaluable for self-improvement and artistic development.
EXIF data, often embedded in images, holds crucial details like camera settings and location. This information, while seemingly insignificant, can be incredibly useful in certain contexts, like verifying the authenticity of products in e-commerce apps, E-commerce apps for instance. Ultimately, understanding and utilizing EXIF data can enhance trust and transparency in various online marketplaces.
EXIF Data in Forensics
EXIF data plays a critical role in forensic investigations, particularly in cases involving image evidence. The metadata can provide crucial clues about the acquisition and manipulation of images. For instance, the date and time of image capture can pinpoint the timeframe of an event, while the location data can place a suspect at the scene of a crime.
Forensic experts can utilize EXIF data to determine if an image has been altered or tampered with, helping to establish the authenticity and reliability of the evidence. In a hypothetical scenario, if a crime scene photo shows suspicious modification, analyzing the EXIF data could reveal whether the alterations occurred before or after the crime.
EXIF Data in Image Editing
EXIF data can be crucial in the image editing process. By retaining the original metadata during edits, the history of changes and the original context of the image are preserved. This helps maintain the integrity of the image, especially when used as evidence or in professional contexts. It is important for maintaining the accuracy and traceability of edits to images, enabling an accurate reconstruction of the original image.
EXIF Data and Image Databases
EXIF data significantly enhances the utility of image databases by providing valuable metadata about the images. This metadata enables sophisticated searching, filtering, and organization of vast image collections, streamlining workflows for professionals and enthusiasts alike. Image databases leverage EXIF data to understand the context behind each image, enriching the user experience.
EXIF Data in Metadata Management Systems
EXIF data acts as a crucial component within metadata management systems for image databases. These systems organize and categorize images based on a wide array of attributes, with EXIF data playing a pivotal role. EXIF data’s structured format allows for seamless integration into database schemas, enabling efficient searching and retrieval.
Benefits of Using EXIF Data for Searching and Retrieving Images
EXIF data facilitates efficient image retrieval by providing searchable s. For instance, a user can search for images taken on a specific date, at a particular location, or with a particular camera model, significantly reducing the time needed to locate specific images. The ability to refine searches with EXIF data accelerates the process of finding desired images. Furthermore, these search capabilities enhance the usability of image databases, especially for large collections.
Using EXIF Data to Filter and Sort Images
EXIF data allows for flexible filtering and sorting of images within databases. Users can readily sort images based on the date they were taken, the time of day, the camera model used, or even the focal length. These sorting options provide a convenient method for organizing and reviewing image collections, streamlining the workflow for various applications. Furthermore, users can filter images based on these attributes to isolate specific subsets of images for specific tasks.
EXIF Data Structure in a Database
A typical database schema for EXIF data would store each tag as a separate field. Each field would contain the tag name and its corresponding value. For example, a field might be named “DateTimeOriginal” and hold the date and time the image was taken. Another field, “GPSLatitude,” might contain the geographical coordinates where the image was captured. This structured approach allows for efficient querying and retrieval of specific EXIF data points.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, EXIF data offers a wealth of information about digital images, providing insights into capture details and history. From extraction and modification to security and legal considerations, this exploration illuminates the importance of understanding this metadata. Its applications are vast, spanning photography, journalism, forensics, and beyond.
Q&A
What is the difference between EXIF and IPTC metadata?
EXIF data is specific to camera settings and image capture details, while IPTC metadata is used for image description and s.
How can I remove EXIF data from an image?
Various image editing software and online tools offer methods to remove or modify EXIF data. Specific steps will vary depending on the software.
Can EXIF data be used for image authentication?
Potentially, but not reliably. While EXIF data can offer clues, it’s not a foolproof method for authenticating an image due to the possibility of manipulation.
What are the common security risks associated with EXIF data?
Malicious actors can potentially exploit EXIF data to track subjects or identify locations, leading to privacy violations.





