How to remove blemishes in Photoshop? This guide dives into various techniques, from basic tools like the Healing Brush to advanced strategies for complex imperfections. We’ll cover everything from understanding image resolution to correcting color inconsistencies after removal.
Mastering these methods allows you to seamlessly polish your images, enhancing realism and visual appeal. The guide provides a comprehensive approach to image enhancement, catering to different skill levels and image types.
Introduction to Photoshop Blemishes
Blemishes, imperfections in the skin’s texture, come in various forms, from small spots and scars to larger marks. Common types include acne scars, blemishes from sun exposure, age spots, and minor imperfections. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the appropriate Photoshop tools and techniques for their removal. Photoshop offers a range of tools designed to address these concerns, often through a combination of techniques rather than a single tool.Photoshop offers a suite of tools to address these skin imperfections.
A strategic approach combining these tools yields optimal results. The efficiency of the removal process hinges on factors like the type and severity of the blemish, the image’s resolution, and the image format.
Photoshop Tools for Blemishes
Various tools in Photoshop are instrumental in blemish removal. The Clone Stamp Tool, Healing Brush Tool, and Spot Healing Brush Tool are frequently used for precise and effective blemish removal. The Clone Stamp Tool duplicates pixels from a source area, blending them seamlessly with the target area. The Healing Brush Tool analyzes the surrounding pixels, replicating their characteristics in the affected area, creating a more natural repair.
The Spot Healing Brush Tool offers a quicker, simpler method for removing small blemishes. These tools allow for selective editing and a variety of blending options to ensure natural-looking results.
Image Resolution and Blemishes
Image resolution significantly impacts the quality of blemish removal. Higher resolution images provide more detail, allowing for finer adjustments and a greater degree of precision when removing blemishes. Low-resolution images may result in pixelation and a less natural appearance after blemish removal. This is due to the reduced number of pixels available for manipulation. Understanding this relationship is vital to choosing the appropriate resolution for a given project.
Image File Formats and Blemishes
Different image file formats have varying degrees of suitability for blemish removal. Formats like TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) are known for their ability to retain high quality details during editing. This is critical when intricate blemish removal is required. Formats like JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) can lead to image degradation if excessive editing is performed.
This is because JPEG uses lossy compression, which can lead to a loss of data during the process. Choosing the appropriate file format beforehand can significantly impact the outcome. JPEG is suitable for sharing or distribution where compression is acceptable.
Suitable Image File Formats
Image formats are important in the blemish removal process. TIFFs maintain the highest quality during editing. They are best for complex edits or when retaining the original quality is paramount. PNGs, with lossless compression, offer an excellent alternative. JPEGs, while convenient for web use, are not ideal for intensive editing because of their lossy compression.
The best format choice depends on the intended use and the level of editing required.
Basic Blemishes Removal Techniques
Mastering blemish removal in Photoshop involves understanding the nuances of different tools. Effective use of these tools ensures natural-looking results, minimizing the appearance of imperfections without altering the overall image’s texture. Each technique offers unique advantages, and the best approach often depends on the type and location of the blemish.The Healing Brush, Spot Healing Brush, and Clone Stamp tools are foundational for blemish removal.
Careful application of these tools, coupled with a practiced eye for detail, is key to achieving flawless results.
Healing Brush Tool: Removing Superficial Blemishes
The Healing Brush tool is ideal for removing small, superficial blemishes that don’t significantly disrupt the surrounding skin texture. Its core functionality involves sampling a flawless area and using that as a reference to replace the blemish. This process is especially effective for blemishes that are relatively isolated and don’t blend seamlessly with the adjacent skin tones.
- Select the Healing Brush Tool: In the toolbar, locate the Healing Brush icon. Adjust the brush size to match the size of the blemish.
- Select a Sample Area: Click and hold on a nearby area of flawless skin. This sample area will be used as the replacement for the blemish. The sample will be slightly transparent, allowing you to see the original blemish and the replacement.
- Brush Over the Blemish: With the sample area selected, brush over the blemish. The tool will automatically blend the flawless skin tone from the sample into the affected area. The tool should blend seamlessly and avoid obvious “patched” areas.
- Adjusting the Tool: Adjust the brush size, opacity, and flow as needed to achieve a natural blend. A lower opacity and flow will allow you to see the adjustments, while a higher opacity will produce a more aggressive result. Experiment with these parameters to refine the outcome.
Spot Healing Brush Tool: Quick Blemish Removal
The Spot Healing Brush tool is a faster alternative for removing isolated blemishes. It’s particularly useful for small, simple imperfections that don’t require precise blending. The tool automatically selects and samples the surrounding area, making the replacement process relatively quick and efficient.
- Select the Spot Healing Brush Tool: Locate and select the Spot Healing Brush tool in the toolbar.
- Brush Over the Blemish: Click directly on the blemish. The tool will automatically sample and replace the blemish with the surrounding skin tone. Adjust the brush size to ensure that the blemish is completely covered, yet avoid over-sampling neighboring areas.
- Adjusting the Tool: Use the brush size and opacity settings to refine the removal. Lower opacity will allow you to see the effects of your adjustments, while higher opacity will result in a more aggressive removal.
Clone Stamp Tool: Removing Blending Blemishes
The Clone Stamp tool is best for removing blemishes that seamlessly blend with the surrounding area. This method works by copying and pasting pixels from one area to another. This is effective for blemishes that have a similar color and tone to the surrounding skin. It provides the most control over precise replication.
- Select the Clone Stamp Tool: Locate the Clone Stamp tool in the toolbar.
- Select a Source Area: Click and hold on a flawless area adjacent to the blemish. This will be your source area for the replacement.
- Brush Over the Blemish: With the source area selected, brush over the blemish, copying the pixels from the source area to the affected area. Carefully adjust the brush size and opacity to maintain a seamless transition between the original and the replacement.
- Adjusting the Tool: Use the brush size, opacity, and flow settings to create a precise and natural blend. For better results, experiment with the different settings.
Advanced Blemishes Removal Strategies
Tackling blemishes in high-resolution images requires a nuanced approach beyond basic techniques. Advanced strategies leverage Photoshop’s powerful tools to achieve a seamless and natural result, minimizing the impact of imperfections without compromising the overall image quality. This section delves into refined methods, including the meticulous use of the Patch tool and the versatile Content-Aware Fill, highlighting their respective strengths and limitations.High-resolution images, often presenting finer details, demand precision in blemish removal.
Removing blemishes in Photoshop is a breeze with the right tools. Mastering techniques like the Healing Brush tool and Spot Healing Brush is crucial, but understanding the broader context of Photoshop’s capabilities is key. For a deeper dive into the essential tools, check out this helpful guide on Top 10 Photoshop Tools You Need to Know.
This knowledge will help you fine-tune your blemish removal process and unlock a wider range of editing possibilities.
A careless application of basic tools can introduce artifacts or leave behind unwanted traces, thus compromising the aesthetic appeal of the final product. Advanced strategies focus on blending the correction seamlessly into the surrounding area, mimicking the natural flow of the image.
Patch Tool for Complex Blemishes
The Patch tool in Photoshop is a powerful instrument for addressing complex blemishes. It allows for precise selection and replacement of affected areas with surrounding pixels. This method is particularly effective for blemishes that exhibit intricate patterns or significant size variations.Using the Patch tool for complex blemishes involves carefully selecting the area encompassing the blemish and then defining a source area that mirrors the surrounding texture.
By using the tool’s brush, a precise selection is achieved, and a replacement from the source area is generated. This method minimizes artifacts and maintains a natural transition. This approach requires practice to master the delicate balance between selection and replacement. An accurate selection of the source area is key to preventing unnatural-looking results.
Content-Aware Fill for Larger Blemishes
Content-Aware Fill, a sophisticated feature, excels at removing larger blemishes and areas of damage in high-resolution images. It’s especially valuable when the affected area is significant and involves substantial loss of detail.The method leverages the image’s surrounding context to fill in the gap left by the removed blemish. Photoshop analyzes the surrounding pixels and generates a seamless replacement. This approach is remarkably effective in seamlessly integrating the restoration with the surrounding environment.
It’s important to note that the quality of the fill is highly dependent on the surrounding image details. Images with complex patterns or limited detail might result in less convincing results. A critical consideration is the surrounding area’s complexity; simpler areas yield more effective results.
Comparison of Blemishes Removal Tools
| Tool | Effectiveness | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Patch Tool | Excellent for intricate and detailed blemishes, especially in high-resolution images. Offers precise control over the replacement process. | Can be time-consuming for large areas. Requires skill and precision for optimal results. May introduce artifacts if the selection isn’t precise. |
| Content-Aware Fill | Highly effective for removing larger areas of damage or blemishes. Efficient for quickly addressing significant imperfections. | May not produce the most natural results in complex areas with intricate patterns or limited detail. Can introduce subtle inconsistencies if the surrounding context isn’t sufficiently representative. |
This table offers a concise comparison of the Patch Tool and Content-Aware Fill, highlighting their strengths and limitations. This helps in choosing the most appropriate tool based on the specific blemish type and image characteristics.
Specialized Blemishes
Tackling specific skin imperfections, such as acne scars and intricate blemishes, requires nuanced Photoshop techniques. These methods often involve a blend of selective adjustments and sophisticated masking strategies to achieve natural-looking results without compromising image integrity. Understanding the unique characteristics of different imperfections is key to selecting the right approach.
Acne Scars
Acne scars, ranging from shallow depressions to raised, hypertrophic marks, demand targeted removal. Strategies for addressing these scars often involve a combination of cloning, healing brush tools, and smart object manipulation. Careful attention to light and shadow patterns is crucial to avoid creating unnatural or jarring results.
Intricate Blemishes
Images with complex details, such as those featuring fine lines, wrinkles, or intricate patterns, present a unique challenge. A gradual and precise approach is essential to prevent blurring or altering the intended aesthetic. Using a combination of high-resolution previews, selective masking, and brush refinement tools can help maintain the image’s overall integrity.
Layer Masks and Adjustment Layers
Layer masks and adjustment layers are indispensable tools for refined blemish removal. Layer masks allow for non-destructive editing, enabling the user to selectively apply adjustments without impacting the rest of the image. Adjustment layers offer further control, permitting nuanced adjustments like brightness, contrast, or color saturation to specific areas of the image. This approach provides flexibility and control, allowing for a more precise and subtle removal of blemishes.
Comparative Analysis of Tools
The effectiveness of various Photoshop tools in addressing different types of blemishes varies. The table below offers a general comparison, recognizing that the optimal choice often depends on the specific imperfection and image characteristics.
| Blemished Type | Recommended Tools | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Shallow Acne Scars | Healing Brush, Clone Stamp, Patch Tool | These tools excel at seamlessly blending the scarred area with surrounding skin, mimicking natural skin texture. |
| Deep Acne Scars | Spot Healing Brush, Content-Aware Fill | Content-Aware Fill can intelligently fill in the area based on surrounding information, minimizing the visible scar. |
| Intricate Blemishes (e.g., wrinkles) | Healing Brush (with low opacity and brush size), Clone Stamp (small brush), Smudge Tool | Using low opacity allows for a gradual and precise blend, preventing blurring. |
| Color Variations (e.g., redness) | Patch Tool, Adjustment Layers (Hue/Saturation), Selective Color | Patch Tool for larger areas, Adjustment Layers for targeted color correction. |
Color Correction and Blending
Color correction and blending are crucial steps in blemish removal to ensure a natural and seamless result. Incorrect color adjustments can leave noticeable artifacts, while poor blending can create jarring transitions between the repaired area and the surrounding skin. This section will Artikel techniques for achieving a realistic and aesthetically pleasing outcome.
Color Inconsistency Correction
After removing a blemish, the surrounding skin tones may appear slightly off. This is a common issue, particularly if the removal process altered the underlying color balance. To address this, employ the “Patch” tool, adjusting its size to encompass the affected area. By sampling the surrounding skin tones, you can fine-tune the color of the repaired area.
This ensures that the corrected section matches the existing color harmony of the image. Using the “Hue/Saturation” adjustment layer allows for precise control over the color values, enabling the adjustment of specific color components.
Blending Techniques for Seamless Integration
Blending the repaired area with the surrounding image is paramount for a natural look. The “Healing Brush” tool is highly effective for seamlessly blending the removed blemish with the surrounding skin, as it samples the textures and colors from the area immediately around the blemish. This method often yields a very natural result. The “Clone Stamp” tool can also be used to blend the area by sampling the surrounding colors and textures.
Adjusting the brush size and opacity can achieve a gradual transition. The use of a “Gaussian Blur” filter, applied subtly, can soften the edges of the repaired area, providing an even more seamless integration.
Maintaining Texture and Detail
Preserving the texture and detail of the image is critical. Over-aggressive editing can result in an unnatural, plastic appearance. Ensure that the repaired area maintains the same texture as the surrounding skin. This is especially important when working with skin tones. Using the “Content-Aware Fill” feature can intelligently fill in the repaired area, often preserving textures and details effectively.
Furthermore, the use of non-destructive editing techniques, like adjustment layers, allows for easier adjustments and prevents the loss of original detail. It’s vital to keep the image’s original quality in mind to avoid the appearance of artificiality.
Avoiding Unnatural Results
To avoid unnatural or jarring results, it’s crucial to work gradually and carefully. Avoid using extremely large brush sizes with the “Healing Brush” or “Clone Stamp” tools. Employ a graduated approach, starting with small brush sizes and progressively increasing them as needed to blend the repaired area. Also, pay close attention to the lighting and shadows in the image.
Mismatches in lighting can create noticeable artifacts, making the repair visually jarring. If needed, use the “Curves” or “Levels” adjustment layers to fine-tune the lighting and shadows in the repaired area, ensuring harmony with the rest of the image. Always evaluate the result critically to maintain realism and avoid any unwanted artifacts.
Understanding Image Backgrounds
The background of an image plays a crucial role in blemish removal. A simple, plain background allows for precise and targeted adjustments. Conversely, a complex background with intricate details, textures, or overlapping elements requires more nuanced techniques to avoid unwanted artifacts. Understanding the background’s characteristics is key to successful blemish removal.The background’s complexity and elements directly impact the selection and application of tools and strategies.
Sophisticated tools are often required to address challenges posed by a busy or detailed background, ensuring a seamless removal of blemishes without introducing visible alterations to the surrounding image elements.
Background Influence on Blemish Removal Techniques
Different background types necessitate distinct approaches. A solid-colored background offers a straightforward path for blemish removal, as the lack of intricate details minimizes the risk of introducing artifacts. However, backgrounds with textures, patterns, or high-contrast areas require more sophisticated techniques to achieve the same level of precision.
Different Background Types and Appropriate Methods
| Background Type | Appropriate Blemish Removal Method |
|---|---|
| Solid color | Simple cloning, healing brush, or content-aware fill |
| Textured | Healing brush with a larger brush size and lower opacity, or content-aware fill with careful adjustments |
| Complex/Cluttered | Using a combination of tools, such as the healing brush, spot healing brush, and potentially content-aware fill with selective masking |
| Transparent/Semi-transparent | Using the healing brush with a very low opacity, or clone stamp with a small brush size and sampling from nearby areas |
Removing Blemishes Near or Overlapping with Complex Backgrounds
When blemishes are situated near or overlap with intricate background details, conventional methods might introduce visible artifacts. Advanced techniques like the healing brush and the spot healing brush become particularly helpful. Using a small brush size and sampling from the surrounding area, ensuring a seamless integration, is critical. These techniques help match the color and texture of the background, minimizing noticeable changes.
Procedure for Removing Blemishes from a Busy, Cluttered Background
This detailed procedure Artikels the process for blemish removal in a busy, cluttered background:
- Initial Assessment: Evaluate the complexity of the background and the position of the blemish. Identify areas with similar textures and colors to the blemish for sampling.
- Selection of Tools: Choose appropriate tools like the healing brush, spot healing brush, or content-aware fill, based on the background’s complexity and the blemish’s size and characteristics. The spot healing brush is excellent for smaller blemishes. For larger areas, content-aware fill is more suitable.
- Sampling and Application: Carefully sample areas close to the blemish that share similar textures and colors. Use a smaller brush size for the healing brush and spot healing brush, adjusting opacity to achieve seamless blending with the background. Employ a soft edge or feathering for the brush strokes to prevent hard edges.
- Refining Adjustments: If needed, refine the result using the adjustment layers (e.g., opacity and blending modes) to further blend the blemish removal with the background.
- Evaluation and Iteration: Evaluate the result thoroughly. If necessary, iterate through the previous steps, adjusting the brush size, opacity, and sampling points until the blemish is effectively removed without introducing artifacts. Repeat steps 2-4 as needed to ensure the blemish is fully concealed and the surrounding area appears seamless.
Preventing Artifacts and Issues
Careful blemish removal in Photoshop necessitates a keen eye for detail to avoid unwanted artifacts. Unnatural results can detract from the overall image quality, so a meticulous approach is crucial. This section Artikels strategies to maintain the integrity of the original image while effectively addressing blemishes.Maintaining the natural look and feel of the image is paramount. Artifacts, such as blurring, softening, or color inconsistencies, can ruin the image’s authenticity.
Understanding how to avoid these pitfalls will yield superior results.
Removing blemishes in Photoshop is often straightforward, but mastering techniques like healing brushes and spot healing tools can take your image editing to the next level. Exploring advanced Photoshop tips, like using layer masks for precise blemish removal, can significantly enhance your workflow. Advanced Photoshop tips offer powerful solutions for more intricate blemishes, allowing for subtle and natural corrections.
Ultimately, these more advanced techniques will help refine your blemish removal skills, leading to polished and professional results.
Minimizing Blurring and Softening
Preserving the sharpness of surrounding areas is vital. Overzealous editing can lead to a blurry effect, making the image appear less detailed. Employing a gentle touch, along with careful brush adjustments, is key to achieving a seamless result. Techniques such as using a high-resolution image as a starting point, and working on smaller areas, are recommended.
Preserving Image Sharpness and Detail
Maintaining the image’s sharpness and detail is paramount for a natural appearance. Avoid excessive blurring or smoothing tools, as these can diminish the texture and fine details of the image. Employing high-quality images, working on small areas, and using appropriate sharpening tools can help retain the original detail. The selection of a proper sharpening tool is important.
Preserving the Original Color Palette
The color palette of the original image should be preserved as closely as possible. Unintentional color shifts or inconsistencies can make the image look unnatural. Using the image’s color information is crucial to avoiding these problems. Employing color adjustment tools cautiously and making adjustments gradually are recommended. This includes using the ‘Content-Aware Fill’ tool selectively, only where necessary to maintain the overall image’s color profile.
Adjusting Brush Settings and Tools
Mastering brush settings is crucial for achieving precise and natural-looking blemish removal in Photoshop. By understanding and adjusting parameters like size, opacity, flow, and hardness, you can significantly enhance the quality of your retouching. This section delves into the intricacies of these settings, providing practical guidance and examples for effective blemish removal.
Brush Size and Opacity
Brush size directly impacts the area affected by each stroke. A smaller brush is ideal for fine details, while a larger one is suitable for covering larger blemishes. Opacity determines the intensity of the brush’s effect on the image. Lower opacity allows for subtle adjustments, while higher opacity creates a more pronounced impact. Precise control is paramount in blemish removal; selecting the appropriate size and opacity is essential for a natural-looking result.
Brush Flow and Hardness, How to remove blemishes in photoshop
Flow determines how quickly the brush color is applied. Higher flow speeds up the application process. Hardness affects the edge definition of the brush stroke. A hard brush produces a sharp, well-defined edge, whereas a soft brush results in a more gradual transition. Adjusting flow and hardness enables you to create a seamless blend with the surrounding skin, achieving a natural finish.
Brush Settings for Different Blemish Types
Different blemish types necessitate different brush settings. For example, small, pinpoint blemishes might benefit from a small, high-opacity brush with a hard edge. Larger, more diffuse blemishes might require a larger, lower-opacity brush with a soft edge to avoid harsh transitions. Consider the size, shape, and depth of the blemish when selecting appropriate brush settings.
Practical Examples of Brush Settings
| Blemish Type | Brush Size | Opacity | Flow | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small, pinpoint pimple | Small (1-3 pixels) | High (80-100%) | Medium (50-75%) | Hard (100%) |
| Large, acne scar | Medium (5-10 pixels) | Low (20-50%) | Low (20-40%) | Soft (0-50%) |
| Redness around a blemish | Small (2-5 pixels) | Medium (50-75%) | Medium (50-75%) | Soft (0-50%) |
These examples illustrate how the choice of brush settings can significantly influence the final outcome. Experimentation with various settings is key to mastering blemish removal. The crucial point is to match the brush settings to the specific characteristics of each blemish.
Image Preparation for Blemishes Removal
Proper image preparation is crucial for successful blemish removal in Photoshop. Optimized images allow for smoother, more effective editing, minimizing artifacts and ensuring a natural-looking result. This section details pre-processing steps to maximize the potential of your blemish removal workflow.Image preparation involves more than just opening the file. Careful attention to resolution, format, and image adjustments will significantly impact the quality of your final result.
It’s a fundamental step that often determines the success or failure of a project.
Image Resizing and Resolution Adjustments
Image resizing and resolution adjustments are vital for optimizing images for blemish removal. Maintaining a balance between image size and detail is key. Resizing an image alters its dimensions, while resolution adjustments influence the amount of detail captured per unit area. The optimal approach depends on the intended use and the complexity of the blemishes.
- Image resizing is important for reducing file size without significant loss of detail. Selecting the right resizing method, such as bicubic interpolation, is important to maintain image quality. Using the correct method will prevent undesirable pixelation and maintain image integrity.
- Resolution adjustment is crucial for specific blemish removal techniques. High resolution is preferred for complex blemishes, while lower resolution may be suitable for simpler cases or when dealing with large images. A higher resolution provides more data for precise detail, which is helpful for advanced editing techniques, but also leads to larger file sizes. Consider the trade-off between file size and image detail.
Preparing Images for Different Blemishes Removal Techniques
The best approach for preparing an image varies depending on the technique employed. Different methods require varying levels of image preparation.
- For cloning or healing brush techniques, maintaining a high resolution and a smooth tonal range is essential. This allows for a more natural blend and minimizes the appearance of artifacts.
- When using content-aware fill, appropriate image resizing and sharpening are necessary to ensure a seamless integration of the repaired area with the surrounding image. Sharpness is essential for avoiding any visual distortions in the edited area.
- When working with specialized techniques such as the patch tool or the spot healing brush, the resolution and the image’s sharpness are critical. High resolution and sharpness are essential to avoid the appearance of rough edges or pixelation around the repaired area.
Best Image Formats and Resolutions for Optimal Results
Selecting the appropriate image format and resolution is essential for achieving the best results in blemish removal. A table below provides guidance for different scenarios.
| Image Format | Resolution (PPI) | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|
| JPEG | 300-600 PPI | General purpose blemish removal, when file size is a concern |
| TIFF | 300-600 PPI | High-quality blemish removal requiring precise details; archival work |
| PNG | 300-600 PPI | Detailed blemish removal, preserving transparency; when lossless compression is required |
Troubleshooting Common Issues: How To Remove Blemishes In Photoshop
Removing blemishes in Photoshop can sometimes lead to unexpected results. Understanding potential pitfalls and how to address them is crucial for achieving natural-looking and professional-quality edits. This section details common problems and effective solutions, tailored to various image types and tools.
Identifying Artifacts
Artifacts, such as halos, color shifts, or unnatural textures, can occur during blemish removal. These artifacts often manifest as visible inconsistencies around the edited area. Careful attention to brush settings and image preparation is key to minimizing their appearance.
Addressing Blurring Issues
Blurring can result from inappropriate brush sizes or intensities, particularly when working with fine details. The Healing Brush and Spot Healing Brush, when used incorrectly, can inadvertently soften the image, obscuring the subject’s texture. Adjusting brush settings, and applying a sharpening filter strategically can help mitigate blurring.
Dealing with Unnatural Results
Unnatural results stem from mismatched tones or colors in the edited area. If the removal process does not blend the edited pixels seamlessly with the surrounding skin, it can create a noticeable mismatch. Using blending modes and color correction techniques can often solve this. Furthermore, careful consideration of the image’s lighting and overall color palette can lead to more subtle and convincing results.
Troubleshooting the Healing Brush
The Healing Brush, while powerful, can create issues if not used appropriately. Problems arise when the brush samples an area too far from the blemish or when the brush size is too large. To mitigate these problems, choose a source area that is visually close to the blemish and use a smaller brush size for precision.
Consider using the “Content-Aware Fill” feature if possible, for a smoother result when dealing with complex blemishes or areas.
Troubleshooting the Spot Healing Brush
The Spot Healing Brush is useful for smaller blemishes, but can cause problems if not used with precision. Overuse of the brush or improper sampling can lead to noticeable inconsistencies. Employing a smaller brush size, using the ‘Clone Stamp’ tool, and applying a mask can refine the edits. Consider the tool’s adaptive nature and its limitations in specific image scenarios, like high contrast areas.
Addressing Issues Specific to Image Types
Different image types pose unique challenges. High-resolution images with intricate details require greater precision than low-resolution images. Images with heavy texture or significant contrast can also require more sophisticated techniques to avoid artifacts. Adjust your approach based on the image’s characteristics to ensure optimal results.
Solutions for Different Image Backgrounds
The complexity of the background plays a crucial role in blemish removal. Images with intricate patterns or textures may require more specialized techniques to avoid artifacts. For example, when dealing with complex backgrounds, consider using a masking strategy or a blend mode to ensure a smooth transition. For simpler backgrounds, a straightforward approach using the Healing Brush might suffice.
Optimizing Brush Settings
Brush settings significantly influence the outcome of blemish removal. Understanding brush size, opacity, and flow is crucial for creating seamless results. The choice of brush settings depends on the size and nature of the blemish, as well as the image’s overall texture.
Examples and Demonstrations
Illustrative examples are crucial for grasping the practical application of blemish removal techniques in Photoshop. Visual demonstrations provide a tangible understanding of how various tools and strategies work in real-world scenarios. This section presents before-and-after images, each accompanied by a detailed explanation of the steps involved in the blemish removal process.These examples showcase the diverse range of tools and techniques available in Photoshop, emphasizing the versatility and flexibility of the software.
Understanding these examples will empower you to confidently address various blemish types and image conditions.
Before-and-After Image Examples
The following examples highlight the application of different tools and techniques in Photoshop for blemish removal. Each example illustrates a specific technique and the noticeable improvement in the image quality.
- Example 1: Using the Healing Brush Tool for a Small Blemish
- Before: An image featuring a small, light-colored blemish on the cheek of a person. The blemish stands out against the skin tone.
- After: The Healing Brush Tool has been employed to carefully blend the blemish with the surrounding skin tones. The blemish is nearly imperceptible.
- Explanation: The Healing Brush tool samples the texture and color from an area of the skin near the blemish. This sampled data is then used to replace the blemish. Precision and careful brush strokes are essential to achieve a natural-looking result.
- Example 2: Spot Removal Tool for a Large Dark Spot
- Before: An image containing a larger, dark-colored blemish, perhaps a freckle or a small birthmark, that significantly differs in color from the surrounding skin.
- After: The Spot Healing Brush tool is used to blend the area, matching the surrounding skin color and tone. The blemish is minimized in contrast to the background.
- Explanation: The Spot Healing Brush is effective for larger blemishes and works to mask the discoloration by sampling and replacing pixels from surrounding areas. The tool automatically adjusts for subtle variations in texture and color.
- Example 3: Cloning Stamp Tool for a Scar
- Before: An image containing a scar with a noticeable change in skin texture. The scar stands out due to a noticeable difference in skin tone and texture.
- After: The Clone Stamp tool has been employed to seamlessly blend the scar with the surrounding skin by cloning the texture from a comparable area.
- Explanation: The Clone Stamp tool allows for precise cloning of a specific area and is suitable for replicating texture and color from a source point to target locations. The selection of the cloning area and the precision of the brush strokes directly influence the final result.
Detailed Stages of Blemishes Removal
This table Artikels the typical stages involved in blemish removal, illustrating the sequence of actions and the tools typically used at each stage.
| Stage | Description | Tools/Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Image Preparation | Ensuring the image is suitable for blemish removal, optimizing file formats, and ensuring adequate resolution. | File adjustments, cropping, resizing. |
| 2. Initial Blemishes Masking | Identifying and targeting the blemishes to be removed. | Spot Healing Brush, Healing Brush, Lasso tool, Magic Wand tool. |
| 3. Color and Texture Adjustment | Correcting the color and texture around the blemishes to enhance the blending effect. | Adjustment layers, Color Balance, Levels, Curves, Brush tool with various blending modes. |
| 4. Fine-tuning and Refinement | Ensuring the blemish is seamlessly blended with the surrounding skin. | Cloning Stamp tool, Healing Brush tool, Smudge tool. |
| 5. Final Output and Review | Saving the edited image and reviewing the final result. | Image optimization, saving in appropriate format. |
Closure
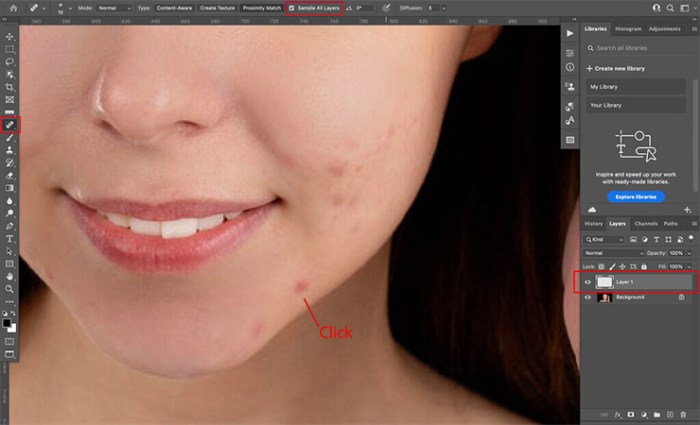
In conclusion, removing blemishes in Photoshop is a multifaceted process. By understanding the diverse tools, techniques, and image considerations, you can achieve professional-quality results. This guide provides a roadmap to navigate the complexities of blemish removal, empowering you to enhance your images with precision and confidence.
Helpful Answers
What are the common types of blemishes?
Common blemishes include acne scars, blemishes, freckles, and other skin imperfections.
How does image resolution affect blemish removal?
Higher resolution images offer more detail for precise blemish removal, while lower resolution images might result in artifacts or blurring.
What are the best image formats for blemish removal?
High-quality formats like TIFF or PSD are generally recommended for detailed editing. JPEGs, while convenient, may have compression artifacts that can interfere with fine details.
What are some common artifacts to avoid during blemish removal?
Artifacts include blurring, softening of surrounding areas, unnatural results, and color inconsistencies. Proper technique and tool usage can help prevent these issues.