Object removal in Photoshop is a powerful technique used across various industries, from product photography to graphic design. This guide delves into the essential methods, from basic selection tools to advanced masking strategies, empowering users to master this versatile skill. We’ll explore different approaches and practical applications, highlighting the importance of precision in achieving professional-looking results.
Mastering object removal in Photoshop unlocks a world of possibilities. From enhancing images to creating compelling visuals, this skill allows you to transform your photos with precision and efficiency. We’ll cover everything from fundamental techniques to sophisticated methods, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently remove unwanted objects from your images.
Selection Techniques
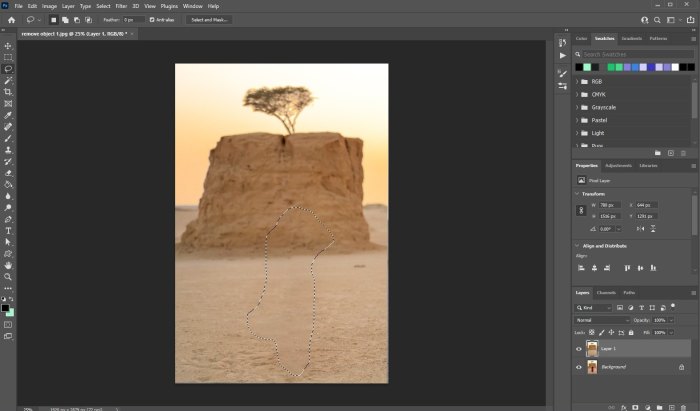
Mastering selection techniques is crucial for precise object removal in Photoshop. Efficient selection methods directly impact the accuracy and speed of the editing process. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various tools empowers you to choose the optimal approach for different scenarios.The choice of selection tool often depends on the complexity of the object to be removed and the desired level of precision.
Some tools excel at quickly selecting simple shapes, while others are better suited for intricate and irregular forms.
Lasso Tool for Complex Selections
The lasso tool, with its various modes (e.g., polygonal, magnetic), allows for highly customized selections, particularly useful for intricate shapes and objects with irregular boundaries. The polygonal lasso creates a series of connected straight line segments. The magnetic lasso follows the edge of an object based on the image’s edge information, adjusting the path dynamically as you move the mouse.
This makes it suitable for objects with distinct edges, significantly reducing the need for meticulous manual tracing.
Magic Wand Tool: Strengths and Weaknesses
The magic wand tool is a quick selection tool that selects pixels with similar colors. Its primary strength lies in its speed and simplicity, making it ideal for selecting large areas of uniform color. However, its weakness lies in its inability to precisely select complex shapes or objects with gradual color transitions. It’s prone to selecting unwanted areas adjacent to the target object due to variations in lighting or subtle color differences.
Pen Tool for Precise Selections
The pen tool offers unparalleled precision in creating custom paths, allowing for the selection of complex and irregular shapes with absolute accuracy. By creating anchor points and adjusting the path with curves, you gain complete control over the selection’s boundary. This control is crucial for removing objects that have intricate details or fine lines.
Quick Selection Tool Compared to Others
The quick selection tool blends the speed of the magic wand with the precision of the lasso. It dynamically adjusts the selection as you paint over the object, offering a good balance between speed and accuracy. It’s particularly effective for objects with relatively smooth edges, while tools like the pen tool offer greater control for complex shapes.
| Selection Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Lasso Tool | High precision for complex shapes, adjustable with different modes | Can be time-consuming for large selections, potentially prone to inaccuracies in complex curves |
| Magic Wand Tool | Fast selection of large uniform areas | Struggles with gradual color transitions, can select unwanted areas |
| Pen Tool | Ultimate precision, customizability for any shape | Most time-consuming selection tool; requires significant user skill |
| Quick Selection Tool | Balance between speed and precision, good for smooth edges | Less precise than pen tool for intricate shapes, can struggle with high contrast |
Content-Aware Fill
Content-Aware Fill is a powerful Photoshop tool that allows users to seamlessly remove objects from an image while maintaining the overall visual integrity of the scene. It works by analyzing the surrounding pixels and intelligently filling in the area where the object was removed, mimicking the surrounding texture and color. This feature is particularly useful for quickly removing unwanted elements without the need for meticulous manual editing.
How Content-Aware Fill Works
Content-Aware Fill leverages sophisticated algorithms to analyze the image’s pixel data in the area surrounding the selection. It identifies patterns, colors, and textures to predict how the removed area should be filled. This predictive modeling is crucial for achieving a natural-looking result. The algorithm effectively blends the surrounding content to create a seamless transition, making the removed object appear as if it never existed.
It essentially re-creates the image based on the existing context, rather than simply filling in the space with a solid color or repeating pattern.
Limitations of Content-Aware Fill
Content-Aware Fill, while versatile, isn’t perfect for all types of objects. It struggles with highly complex or detailed subjects, particularly those that have sharp contrasts or intricate patterns that the algorithm struggles to replicate. Objects with distinct shapes or colors that are repeated elsewhere in the image can lead to artifacts or inconsistencies. For example, if a repeated pattern is present in the area to be filled, it may struggle to blend seamlessly, potentially creating a noticeable repeating pattern or an inaccurate color match.
Highly detailed textures, intricate designs, or large, complex areas of similar content may also result in less accurate outcomes.
Parameters Affecting the Outcome
Several parameters influence the outcome of Content-Aware Fill, impacting the accuracy and naturalness of the result. The size and shape of the selection play a critical role. A smaller, more precisely defined selection generally leads to better results than a large, irregular one. Additionally, the surrounding context is paramount. If the area surrounding the selection has a strong visual pattern or texture, the algorithm will attempt to replicate it.
Object removal in Photoshop can be a time-consuming task, but luckily, there are ways to streamline the process. Exploring top Photoshop plugins and extensions, like those found in Top Photoshop Plugins and Extensions to Boost Creativity , can significantly speed up and enhance object removal techniques. Ultimately, these tools can make complex object removal projects much more manageable.
The “Content-Aware Fill” options within Photoshop offer control over the blending and adjustment of the fill, allowing users to fine-tune the outcome.
Effective Use Cases
Content-Aware Fill excels in situations where a subtle and natural-looking removal is required. Removing minor objects like a stray branch or a small distracting element from a photograph is often handled with ease. Also, scenarios involving filling in gaps in an image, such as removing a missing section of a wall, are often successful. Moreover, situations where the object to be removed is well-integrated into the surrounding environment can result in seamless removal.
Successful and Unsuccessful Applications
| Example | Success/Failure | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Removing a stray tree branch from a landscape photo. | Success | The branch is a simple object with limited detail and is well-integrated into the background. |
| Removing a person from a crowded street scene. | Partial Success | The person’s presence is noticeable, and their attire may be similar to other people in the scene. |
| Removing a damaged section of a building in a historical photo. | Unsuccessful | The missing section of the building has a complex pattern, and the surrounding area does not provide enough context for accurate reconstruction. |
| Filling in a missing section of a wall in a room interior photo. | Success | The surrounding wall has a consistent texture and color, providing adequate context for the algorithm to create a seamless fill. |
Masking Techniques
Masking is a fundamental technique in Photoshop for precisely controlling the application of effects and adjustments. It’s particularly valuable for object removal, allowing you to selectively hide or reveal portions of an image without affecting the surrounding areas. Mastering masking unlocks a level of control that other methods like Content-Aware Fill sometimes can’t achieve.Different masking methods offer varying degrees of precision and speed, catering to diverse needs and complexities of object removal tasks.
This section delves into various masking types, emphasizing their practical applications in Photoshop.
Types of Masks
Masking in Photoshop provides various tools for selectively hiding or revealing portions of an image. Understanding these different types of masks is crucial for achieving the desired results.
- Layer Masks: These masks are linked directly to a layer, allowing precise control over what portions of that layer are visible. This granular control makes them ideal for intricate object removal. For example, when removing a person from a photograph, you can meticulously paint the mask, revealing or hiding portions of the person’s form while preserving the background.
This is often the preferred method for complex removals.
- Quick Masks: These masks offer a more streamlined approach, employing a color-based selection method. They are beneficial for quicker, less intricate object removals. Quick masks allow for a faster selection process compared to traditional selection tools, enabling quicker removal of simple shapes or objects. A quick mask is often useful for objects with clean edges, like a simple object from a flat background.
Object removal in Photoshop is a powerful tool, but its effectiveness hinges on the software’s overall capabilities. Considering the cost, it’s worth exploring if Photoshop, specifically its object removal tools, aligns with your workflow needs, as discussed in depth in Is Photoshop Worth the Price? A Creative’s Perspective. Ultimately, the ease and precision of object removal are key factors in determining Photoshop’s value for any given creative project.
- Channel Masks: Channel masks utilize the color channels of an image to create selections. They are less commonly used for object removal, but their applications exist, especially in more advanced or specific situations. For example, they are sometimes used for creating selections based on the color information of an image, making them relevant when the object to be removed is based on color.
Layer Masks for Precise Removal
Layer masks provide the highest level of control in Photoshop for object removal. They operate by painting black to hide and white to reveal. This gives the user the greatest amount of flexibility. Creating a selection and converting it into a layer mask is a standard approach.
- Creating a Layer Mask: First, make a selection of the object you wish to remove. Then, go to Layer > Layer Mask > Reveal Selection. Alternatively, you can click on the Add Layer Mask icon, which is a white rectangle with a black circle inside.
- Refining the Mask: The real power of layer masks lies in refining the mask’s edges. You can use different brush sizes and hardness to fine-tune the transition between the object and the background. Brush tools allow you to adjust the mask’s edges in areas with a lack of clarity or sharp edges, ensuring the object is seamlessly removed. Soft brushes offer smoother transitions.
- Using Different Brush Modes: Employ different brush modes to address various masking needs. For instance, using a soft brush with a low opacity allows for gradual transitions and subtle edge corrections.
Quick Masks for Quick Removal
Quick masks provide a faster way to select objects. By using a color, usually a vibrant shade like red, you can quickly define the area to be removed. They are particularly beneficial for subjects with defined edges.
- Applying the Quick Mask: Click on the Quick Mask Mode button. The selected area will be highlighted in the designated color.
- Refining the Selection: Use the brush tool to refine the selection by painting over areas that need to be included or excluded. Use the brush tool with different brush modes and sizes to adjust the quick mask.
- Converting to a Layer Mask: After you’re satisfied with the selection, click on the Quick Mask Mode button again to exit quick mask mode. The selection will automatically be converted into a layer mask.
Comparison of Masking Techniques
| Technique | Efficiency | Precision | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Layer Masks | High | High | Medium |
| Quick Masks | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Channel Masks | Low | Medium | High |
Image Preparation
Proper image preparation is crucial for successful object removal in Photoshop. A well-prepared image reduces the complexity of the removal process, minimizing potential artifacts and ensuring a more natural-looking result. This involves considering factors like lighting, contrast, and resolution.High-quality images with optimal lighting and contrast provide the necessary information for the software to accurately replace the removed object with the surrounding environment.
Poor image quality can lead to noticeable gaps, unnatural color shifts, and other undesirable artifacts. Furthermore, understanding the impact of resolution on the outcome is essential for selecting the right image for the task.
Importance of Image Quality, Object removal in Photoshop
High-quality images offer superior detail and information, crucial for precise object removal. This detail allows for a more accurate and seamless replacement of the removed object, resulting in a more natural and polished final image. Conversely, low-quality images can lead to artifacts and inconsistencies in the final result.
Impact of Lighting and Contrast
Lighting and contrast directly influence the accuracy of object removal. Even lighting across the image facilitates smoother transitions and replacements. Strong contrast enhances the definition of edges and details, aiding the software in differentiating the object from the background. Uneven lighting and low contrast can make the removal process more challenging, potentially leading to undesirable artifacts.
Influence of Image Resolution
Image resolution significantly impacts the outcome of object removal. Higher resolution images provide more data for the software to work with, leading to a smoother and more detailed removal process. Lower resolution images can lead to a pixelated or blurry result, especially when removing fine details. The software may struggle to accurately replace the removed object, potentially creating noticeable artifacts or gaps.
Best Practices for Image Preparation
- Use high-resolution images whenever possible. Higher resolution images offer more detail, leading to more precise and natural-looking object removal.
- Ensure even lighting across the image. Uneven lighting can make the removal process more difficult and lead to artifacts.
- Optimize contrast. Sufficient contrast helps the software distinguish the object from the background, resulting in a cleaner removal.
- Consider the complexity of the object to be removed. Complex objects with intricate details might require higher resolution images and more careful lighting.
- Preview the results of your object removal before finalizing the edits. This allows you to identify and correct any potential issues.
Impact of Resolution and Lighting on Results
| Image Resolution | Lighting | Result |
|---|---|---|
| High | Even | Clean, detailed, natural-looking removal. |
| High | Uneven | Potential for artifacts, but still manageable with advanced techniques. |
| Low | Even | Pixelated or blurry removal, potentially showing gaps. |
| Low | Uneven | High probability of artifacts and noticeable gaps, making removal difficult. |
Refine Edge & Smoothness
The Refine Edge tool in Photoshop is a powerful feature for meticulously adjusting selections, particularly crucial for precise object removal. It allows for fine-grained control over the edges of a selection, enabling the removal of objects with intricate details and complex shapes without causing noticeable artifacts. Mastering this tool streamlines the object removal process, significantly enhancing the quality of the final image.
Refine Edge Tool for Precise Object Removal
The Refine Edge tool offers a suite of options for refining the edge of a selection. This enables a smooth transition between the selected area and the surrounding background, eliminating harsh lines and creating a seamless effect. It is instrumental in situations where a hard selection isn’t sufficient, particularly for complex or textured edges.
Options within the Refine Edge Tool
A wide range of options within the Refine Edge tool allows for tailored adjustments. These include brush size, feathering, and smart radius, which directly influence the selection’s edges. The brush size controls the area affected by the adjustment. Feathering softens the selection’s edges, while smart radius intelligently adjusts the radius based on the image’s content.
Refine Mask Tool for Fine-Tuning Selections
The Refine Mask tool provides a non-destructive way to fine-tune the selection created by the Refine Edge tool. By using a mask, you can selectively modify the selection’s edges, making adjustments where needed, without affecting the rest of the image.
Creating Smooth Transitions Around Removed Objects
Achieving smooth transitions around removed objects is a key aspect of professional image editing. Using the Refine Edge tool, adjustments can be made to the selection to seamlessly integrate the removed object’s edges with the background. This results in a more natural-looking effect, where the removal is barely noticeable. Understanding the brush size, feathering, and radius settings within the Refine Edge tool is critical to achieving smooth transitions.
Furthermore, the use of the Refine Mask tool is essential for precision in removing the object without disrupting the surrounding area.
Refine Edge Tool Settings
| Setting | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | Determines the area around the selection that is affected by the refinement. | A larger radius affects a wider area, potentially creating a smoother transition but potentially introducing unwanted blurring or halo effects if not carefully controlled. |
| Feather | Softens the edges of the selection. | Increased feathering results in a more gradual transition, creating a softer, less defined edge. |
| Smart Radius | Automatically adjusts the radius based on the image’s content, identifying and adapting to subtle edges. | This option automatically adjusts the radius based on image details, preventing harsh transitions or unnecessary blurring. |
| Show Mask | Displays the mask created by the Refine Edge tool. | Allows visual inspection of the selection’s mask to confirm and fine-tune the edge adjustments. |
| Brush Size | Controls the size of the brush used to apply the refinement. | A smaller brush size allows for more precise adjustments to smaller details. |
Background Replacement
Replacing the background of an image after object removal is a crucial step in photo editing. A well-replaced background seamlessly integrates the subject into a new setting, enhancing the overall image’s impact. Various methods are available, each with its strengths and limitations, depending on the complexity of the task and the desired aesthetic.
Content-Aware Fill for Background Replacement
Content-Aware Fill leverages Photoshop’s sophisticated algorithms to intelligently analyze the surrounding pixels and predict how to fill the void left by the removed object. This method is particularly effective for complex backgrounds with subtle gradients and textures. The software examines the patterns and colors in the area surrounding the selection and generates a believable replacement. This process is automated and requires minimal user interaction, making it a time-saving solution.
However, the quality of the replacement depends on the complexity of the background. For intricate designs or highly detailed backgrounds, the results might not be perfect.
The Clone Stamp Tool for Background Replacement
The Clone Stamp tool offers a more manual approach to background replacement. This technique allows precise control over the blending of the new background. Users select a source area with a similar background and paint over the removed object’s space, mimicking the existing texture. This meticulous process is essential for intricate backgrounds, ensuring a seamless blend. However, it demands patience and skill to achieve accurate results, as the user must meticulously match the lighting, textures, and colors.
A great advantage is the ability to produce highly realistic and tailored background replacements.
Using Patterns and Gradients for Background Replacement
Using patterns and gradients offers a straightforward method for background replacement, particularly useful for simple backgrounds. A pattern, for example, can quickly and effectively replace a plain background. A solid color or a gradient, especially with a smooth transition, is often suitable for filling a space. This technique is ideal for images with flat, homogenous backgrounds. The selection of the correct pattern or gradient depends on the desired aesthetic.
Patterns and gradients provide a quick and effective way to change the background to a solid color or a pattern that suits the picture.
Comparison of Background Replacement Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Aware Fill | Fast, automated, good for complex backgrounds | May not produce perfect results for highly detailed backgrounds | Simple to complex backgrounds with subtle gradients and textures |
| Clone Stamp Tool | Precise control, high realism | Time-consuming, requires skill | Intricate backgrounds, where a perfect match is crucial |
| Patterns/Gradients | Fast, easy to implement, suitable for simple backgrounds | Limited to simple backgrounds, less control over the final result | Flat, homogenous backgrounds, solid colors, or patterns |
Advanced Techniques
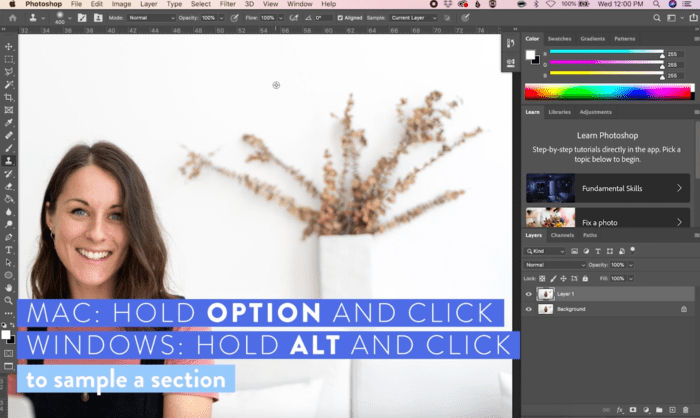
Beyond the fundamental object removal methods, advanced techniques offer greater control and precision, particularly when dealing with intricate subjects or complex backgrounds. These approaches leverage Photoshop’s more sophisticated tools to achieve results that are virtually indistinguishable from seamless image editing.Employing these advanced methods often leads to superior outcomes, especially in scenarios where the object’s shape or the background’s details are intricate.
Mastering these techniques allows for more nuanced adjustments, resulting in higher quality object removal and ultimately, more satisfying results.
Using Adjustment Layers for Object Removal
Adjustment layers offer a non-destructive way to refine object removal. They allow for selective modifications without permanently altering the original image data. By applying adjustment layers, such as curves or levels, specifically to the areas surrounding the removed object, you can enhance the blending and seamlessness of the removal. This is especially beneficial when the removed object is complex and has subtle variations in tone or color.
Using Channels for Precise Selections
Channels in Photoshop can be instrumental for intricate object selections. They offer a more granular way to isolate elements based on color or tonal variations. For example, using a channel that highlights a specific color present only in the object you want to remove allows for a more precise selection. This precision is particularly useful for subjects with fine details or subtle color gradients.
By employing channel masks, users can further refine the selection.
Using Plugins for Object Removal
Various plugins extend Photoshop’s capabilities for object removal. These plugins often offer automated tools or advanced algorithms to improve selection accuracy, speed up the process, or address specific removal challenges. The choice of a plugin depends on the complexity of the removal task and the user’s specific needs. Some plugins can streamline the process by automating tedious steps, while others offer advanced algorithms to create highly accurate selections.
Consider the type of removal and the characteristics of the image for optimal results.
Plugins provide a means to leverage specialized algorithms and tools that are not built into the core Photoshop software. This can enhance the speed and precision of object removal, especially in complex situations.
Troubleshooting
Object removal, while often straightforward, can sometimes present unexpected challenges. Understanding potential pitfalls and their solutions is crucial for achieving optimal results. This section details common problems and their effective resolutions, helping you confidently navigate the process and avoid frustrating roadblocks.
Common Object Removal Problems and Solutions
Troubleshooting object removal issues often involves identifying the root cause of the problem. Careful analysis of the selection, the chosen method, and the image itself can help isolate the difficulty. Here’s a breakdown of common problems and their corresponding solutions:
- Inaccurate Selections: Imperfect selections lead to visible artifacts or incomplete removal. Refinements are necessary to ensure a clean, seamless result. Utilize the Refine Edge tool to fine-tune selection boundaries, particularly around complex edges or textures. Consider using a different selection tool, like the Magnetic Lasso or Pen tool, if the initial selection is problematic. If the object is not completely selected, consider using the quick selection tool and refine the selection edges using the refine edge tool.
- Content-Aware Fill Issues: Content-Aware Fill, while powerful, can sometimes produce unsatisfactory results. This occurs when the surrounding content lacks sufficient detail or texture to effectively fill the gap left by the removed object. Try adjusting the fill radius to allow for more context or, if possible, use a different method such as a background replacement for more control over the result.
If the replacement is still poor, examine the surrounding area for patterns and make sure they are not too repetitive. Ensuring the source area has similar textures or colors is essential for accurate results. If the problem persists, consider manually patching the area with a clone stamp tool to mimic the surrounding pixels more closely.
- Unnatural Results: The object removal may look unnatural or distorted, especially if the method used doesn’t appropriately address the subject’s surrounding environment. This is often related to issues with selection accuracy or a lack of detail in the surrounding area. Ensuring the selected area is well defined and the surrounding environment has sufficient texture to blend with the object’s replacement will help prevent this.
A better selection and more careful adjustments in the refine edge tool are important for getting natural-looking results. Consider increasing the brush size and using multiple strokes in the content-aware fill to get a more natural effect.
- Preventing Common Mistakes: Careful preparation is key to avoiding common pitfalls. Start with a high-resolution image, and ensure the lighting and composition are conducive to successful removal. Ensure the object is clearly defined from the background. Select an appropriate tool for the type of object being removed and the image’s characteristics. A proper selection is vital.
Incorrect selections often lead to a poor outcome. Be mindful of the background and ensure it is suitable for seamless blending. Always check your work and make necessary adjustments.
Troubleshooting Selections
Precise selections are paramount for successful object removal. Errors in selection can lead to incomplete removal, visible artifacts, or an overall poor outcome. Troubleshooting selection issues involves careful analysis of the selection method and its application to the image.
- Selection Tool Selection: Choose the most appropriate selection tool for the object being removed. For simple shapes, the Rectangular or Elliptical Marquee tool might suffice. However, for complex shapes, the Polygonal Lasso, Magnetic Lasso, or Pen tool might be necessary. Different tools are effective for different shapes and complexities.
- Refine Edge Adjustments: The Refine Edge tool allows for precision in selection refinement. Adjusting the feathering, contrast, and smoothness settings ensures a clean and natural transition between the selected area and the background. Using the Refine Edge tool is important to get a seamless blend between the object and the background.
- Selection Issues: If the selection is not accurate, use the selection tool to make necessary adjustments, or refine the edges using the refine edge tool. Incorrect selections often lead to unsatisfactory results. Always check your selection and make necessary adjustments.
Troubleshooting Content-Aware Fill
Content-Aware Fill, while a powerful tool, can sometimes produce unexpected results. Understanding its limitations and how to address them is crucial for achieving satisfactory outcomes.
- Insufficient Detail: The surrounding area must have enough detail to provide a reliable source for filling the gap. Ensure the area surrounding the object has sufficient texture and variation to create a convincing replacement. Increasing the brush size and using multiple strokes can help get a more natural result.
- Unnatural Results: The tool may not accurately predict the texture or patterns surrounding the area. Manually editing the result may be necessary. Try to use the clone stamp tool or a different technique to address the problem. In case of poor results, using different techniques to fill the gap is often necessary.
Preventing Mistakes
Careful preparation and understanding of the object removal process can help avoid many common mistakes.
- Image Resolution: Ensure the image has sufficient resolution to prevent pixelation issues after removal. High resolution images are important for getting a clean result.
- Selection Accuracy: Carefully select the object, paying attention to details and complexity. Use the Refine Edge tool to ensure the selected area is accurate. Using the correct selection tool and making adjustments as needed will help get a good result.
- Background Similarity: If possible, choose an image where the object is contrasted against a background that is sufficiently similar in texture and color. Backgrounds that are similar to the object can cause blending issues.
| Common Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Inaccurate selections | Use Refine Edge, alternative selection tools, or refine the edges using a selection tool. |
| Content-Aware Fill Issues | Adjust fill radius, use background replacement, or manually edit the result using the clone stamp tool. |
| Unnatural results | Ensure proper selection, sufficient detail in the surrounding area, and appropriate adjustments to the selected area. |
Last Recap
In conclusion, object removal in Photoshop offers a diverse range of techniques, catering to varying levels of expertise. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced editor, this guide provides a comprehensive roadmap to achieve flawless results. From simple selections to intricate masking and advanced techniques, this resource equips you with the skills to confidently manipulate images and achieve professional-grade outputs.
Commonly Asked Questions: Object Removal In Photoshop
How can I remove a complex object using the lasso tool?
The lasso tool excels in intricate selections. Use the freehand lasso for freeform shapes, or the polygonal lasso for more precise, angular Artikels. Practice adjusting the anchor points and smoothing the selection to refine your outcome.
What are the limitations of Content-Aware Fill?
Content-Aware Fill performs best with objects that have surrounding context. It may struggle with highly complex or unique shapes, or those lacking sufficient similar surrounding patterns. Always check the results carefully and consider alternative methods if necessary.
What are some common mistakes to avoid during object removal?
Common pitfalls include insufficient image resolution, poor lighting conditions, and inadequate selection precision. Carefully assess your image before starting, and practice precision at each step to prevent unwanted artifacts or distortions.
How do I prepare my image for object removal?
Optimizing image quality significantly impacts the outcome. Ensure the image has good lighting, a clear subject, and sufficient resolution. Improving contrast and detail enhances the selection process.